Introduction to Fyde protocol
What is Fyde ?
Fyde Protocol introduces a trustless treasury management solution that addresses the four pillars of cryptocurrency treasury management: diversification, asset liquidity, yield generation, and governance. It tackles the DAO treasury conundrum by incentivizing users to deposit into a diversified pool of assets, while allowing for the retention of governance rights and preserving direct user control over their allocations.
Fyde introduces an on-chain exchange pool, where tokens over a range of sub-sectors come together to compose a portfolio management strategy—tracking the market performance of each asset and implementing a dynamic weight mechanism that targets a range of volatility metrics (beta-targeting) for the pool.
How it works
The Fyde Treasury is comprised of a single pool of assets. In order for a token to participate in this pool it must first apply for whitelisting. If the token passes through the filtering process and is accepted, any external user can begin to deposit this token into the pool. When an eligible token is listed, a corresponding target concentration will be specified by the protocol. In order for the pool to maintain its asset alllocation strategy, users will be incentivized to bring the token to its proper weight in the pool, and be disincentiveized from straying too far from it. As a result, withdrawing and depositing underweight and overweight tokens, respectively, will incur taxes for the user. Conversely, there won’t be taxes levied for withdrawals/deposits of overweight/underweight tokens. When the pool needs to rebalance assets to meet its concentration targets, token swaps in desirable directions will offer a reward for arbitrageurs by pricing the assets at a discount to the market.
A user can deposit 1-5 tokens simultaneously. They will be priced using an oracle, which consists of a combination of a Chainlink price feed along with a UniswapV3 TWAP (when available). This price is used to mint an equivalent number of TRSY tokens, representing the user’s overall share of the combined holdings of the pool. The user can then choose to burn these tokens with the pool in order to withdraw a group of 1-5 different assets. The user should keep in mind the potential withdrawal taxes when doing this (if the user is withdrawing underweight tokens), and can choose an “Optimal Withdrawal” option in order to receive the combination of tokens that the can be withdrawn with minimal cost.
The user can also choose to retain their governance rights over a particular token. This option is similar to a standard deposit, however, instead of the assets being deposited into the combined holdings of the pool, a separate custodial contract is generated for the user and the tokens are transferred there directly. The proportional value of TRSY is still minted, however, it will be automatically staked on the custodial contract as well—issuing the user “staked TRSY” (stTRSY) instead. This custodial contract allows the user to retain the governance power of these tokens by giving them the ability to choose a wallet address or a Snapshot space to delegate to. The user should keep in mind that the value of this custodial contract is determined by the amount of TRSY tokens staked on it, which means that if the corresponding governance token outperforms/underperforms the value of the overall pool, a proportional number of tokens will be moved from/to the contract to be made available for the deposit/withdrawal/swap actions taken by other users. A user can, at any time, withdraw the contents of the their custodial contract directly by burning their stTRSY. Alternatively, they can unstake their stTRSY and receive TRSY. This action will permanently give up their governance rights, however, they will likely be able to access greater market liquidity if they want to sell the TRSY token.
Architecture
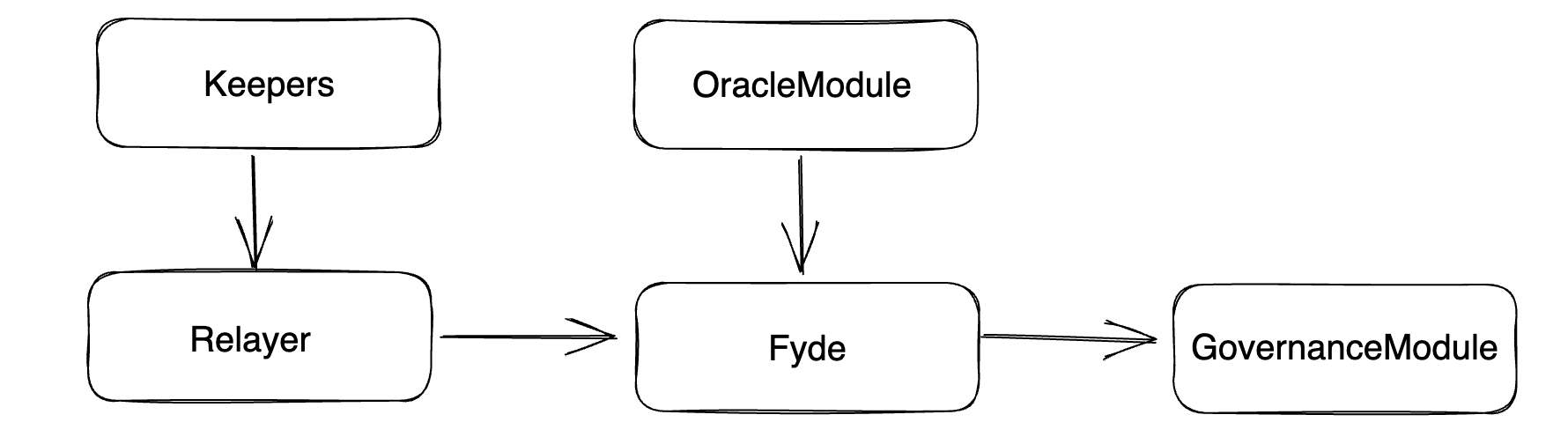
The protocol architecture is composed of four main smart contracts:
- The Relayer: contains the entry points into the protocol for external users, as well as the protocol automation logic.
- Fyde: contains the main logic of the protocol, allowing for depositing, withdrawing, and swapping assets.
- OracleModule: allows for obtaining on-chain pricing of assets.
- GovernanceModule: contains the logic allowing a user to retain governance rights over their assets.